When designing a website with CSS, one of the most common sources of confusion is the difference between padding and margin. Both control spacing, but they serve different purposes. Knowing how and when to use them is crucial for creating clean, well-structured layouts.
In this guide, we’ll break down:
- The key differences between padding and margin
- Visual examples of how each works
- When to use padding vs margin
- Best practices to keep your design consistent
Understanding the CSS Box Model
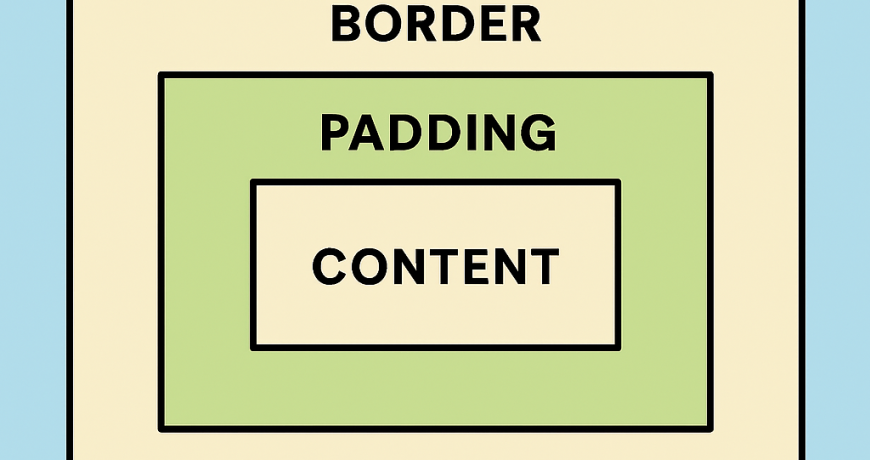
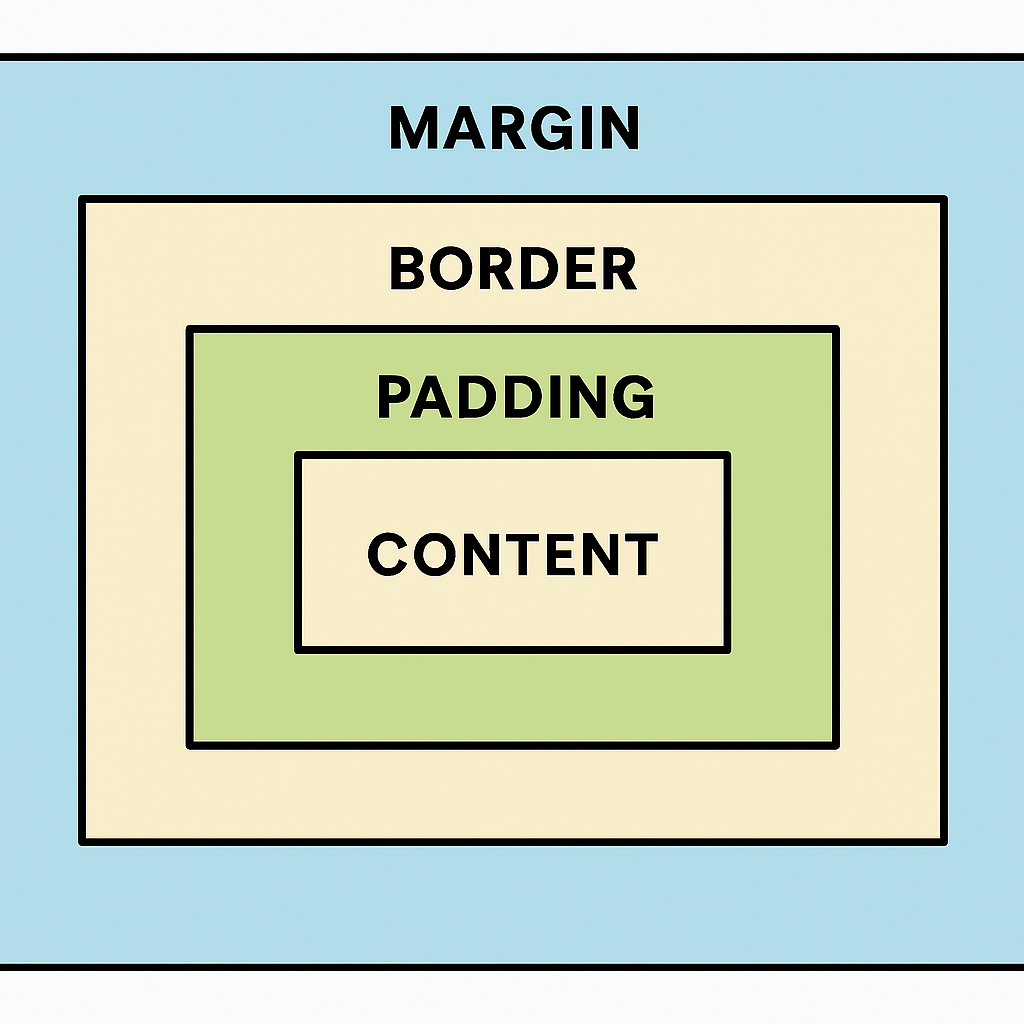
Before diving into padding and margin, it’s important to understand the CSS box model. Every element in a webpage is a rectangular box consisting of:
- Content – The text, image, or data inside the box.
- Padding – The space between the content and the border.
- Border – The edge of the element.
- Margin – The space between the element and surrounding elements.
What is Padding?
Padding is the space between the element’s content and its border. It adds internal spacing within the box, making the content more readable and giving it breathing room.
Example of Padding:
button {
padding: 15px 25px;
}This makes the button larger by adding internal space around the text.
✅ When to use padding:
- To create space inside buttons, input fields, or containers
- To improve readability by giving content breathing room
- To maintain consistent spacing within boxes
What is Margin?
Margin is the space outside the element’s border, separating it from other elements. It creates external spacing and controls the distance between elements on a page.
Example of Margin:
h1 {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}This pushes the heading 20px away from the next element.
✅ When to use margin:
- To create spacing between headings, paragraphs, or sections
- To align elements apart from each other
- To prevent elements from overlapping
Key Differences Between Padding and Margin
| Feature | Padding (Inside) | Margin (Outside) |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Space inside element, between content & border | Space outside element, beyond border |
| Affects Size? | Increases the element’s total size | Does not increase the element’s size |
| Purpose | Creates internal spacing for content | Creates external spacing between elements |
| Common Use | Buttons, forms, containers, text boxes | Headings, sections, layout alignment |
Visual Example
Imagine a card box:
- Padding = space inside the card around the text or image.
- Margin = space outside the card, separating it from other cards or the page border.
When to Use Padding vs Margin
✅ Use Padding When:
- You want to increase clickable/touchable areas (e.g., buttons).
- You need breathing room inside containers (e.g., text inside a box).
- You want to maintain consistent spacing between content and border.
✅ Use Margin When:
- You want to control spacing between multiple elements.
- You need to separate sections (e.g., space between paragraphs).
- You want to center elements using
margin: auto.
Best Practices for Using Padding and Margin
- Be consistent: Use a spacing system (e.g., 4px scale: 4, 8, 16, 32).
- Avoid over-nesting: Too many layers of margin/padding can create layout issues.
- Check responsiveness: Test spacing on mobile and desktop.
- Use CSS variables: For consistent spacing across your design system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I use both margin and padding on the same element?
Yes, you can use both. For example, a button may have padding inside (to enlarge the clickable area) and margin outside (to space it from other buttons).
2. Does padding increase the size of an element?
Yes. Padding increases the total size of an element because it adds space inside the border. For example, a 100px wide box with 20px padding becomes 140px wide.
3. Does margin affect element size?
No. Margin creates space outside the element but does not increase its width or height. It only shifts the element relative to others.
4. Should I use margin or padding for spacing between paragraphs?
Use margin between paragraphs, since it creates external spacing between blocks of text. Padding is better for internal spacing, like inside a highlighted text box.
5. What’s the difference between padding and border-spacing in tables?
- Padding adds space inside each cell (between text and cell border).
- Border-spacing adds space between cells in a table.
6. Is margin collapse still an issue in CSS?
Yes. Vertical margins between block elements (like paragraphs) may collapse into a single margin. To avoid issues, sometimes padding is preferred for vertical spacing.
Final Thoughts
The difference between padding vs margin may seem small, but it makes a huge impact on layout and design. Remember:
- Padding = inside spacing
- Margin = outside spacing
By mastering these two properties and knowing when to use them, you’ll have cleaner, more professional layouts.